Rust と C/C++ プロジェクトで使う IDE を Zed に更新してみました。超高速で大変良い感じです…!
本記事では PlatformIO プロジェクトを Zed で扱う方法を記載します。
Love your editor again
Zed is a minimal code editor crafted for speed and collaboration with humans and AI.
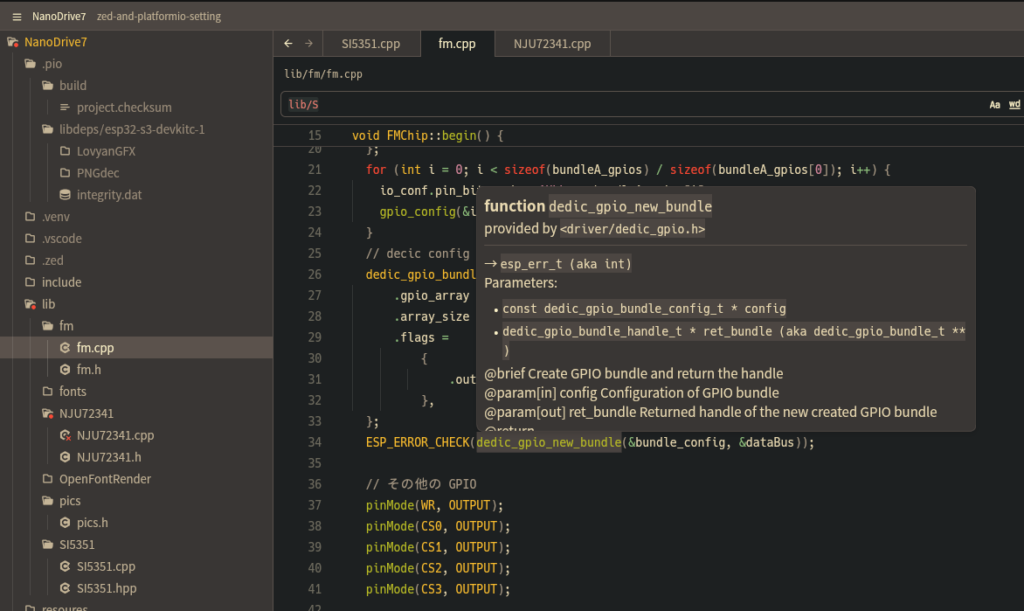
Zed での C/C++ の扱いについてですが LSP として clangd が使われています。このことから cmake などが作り出す compile_commands.json を読ませることで多くの C/C++ プロジェクトを Zed で編集することができます。
2025-12 現在、PlatformIO の生成する compile_commands.json にいろいろ混乱があるようで、この記事の手順にはかなりのハックを含んでいです。PlatformIO が将来改善されている可能性が高いのでその部分はご参考程度です。
Linux で動作確認していますが、他の OS でも同様に構成できるはずです。(Windows が手元になくてそらで書いてますので適宜修正していただければ…)
ここでは Fujix さんの ESP32S3 を使ったスーパーな FM 音源プレイヤーである、NanoDrive7 の PlatformIO プロジェクトを Zed で扱えるようにする例で解説します。
まずは NanoDrive7 の PlatformIO プロジェクトを取得しましょう。もしくは既存の PlatformIO にカレントディレクトリを移してください。
$ git clone https://github.com/Fujix1/NanoDrive7.git
$ cd NanoDrive7
clangd の導入
最初はプロジェクトごとの設定に先行して、C/C++ LSP である clangd を clangd のドキュメントを参考にしながら導入し、 clangd コマンドで起動するように構成します。
Ubuntu の場合:
$ sudo apt install clangd-21
$ sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/clangd clangd /usr/bin/clangd-21 100
$ clangd --version
Ubuntu clangd version 21.1.8 (++20251212093602+51e5074676d4-1~exp1~20251212093735.68)
Features: linux
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
Windows の場合:
おそらく winget で入れるのがお手軽です。以前の記憶では PATH は自動で通らなかったと思うので clangd を探し起動できるようにしてください。
> winget install --id=LLVM.clangd -e
# パスを通して起動できれば OK
> clangd --version
PlatformIO の導入
既に Python に PlatformIO の最新版が導入されていればこの項の手順は不要です。
ここではプロジェクトローカルに最新版の PlatformIO を導入する手順を記載します。Python の venv を使っていますが、最近だと uv のほうがいいのかもしれません。
Linux / macOS の場合:
$ pwd # プロジェクトにカレントディレクトリがあること
/home/hiromasa/devel/esp32/NanoDrive7
$ zed . # Zed を起動する(以下 Zed のターミナルにて)
$ python -m venv .venv
$ source .venv/bin/activate # [[ もしくは Zed ターミナルを再起動 ]]
$ python3 -m pip install -U platformio
$ pio --version
PlatformIO Core, version 6.1.18
Windows の場合:
> pwd # プロジェクトにカレントディレクトリがあること
> zed . # Zed を起動する(以下 Zed のターミナルにて)
> python -m venv .venv
> .venv\Scripts\activate.ps1 # [[ もしくは Zed ターミナルを再起動 ]]
> python3 -m pip install -U platformio
> pio --version
PlatformIO Core, version 6.1.18
Zed は次のデフォルトセッティングにより .venv を認識して自動アクティベートしてくれますので次回 Zed 起動時は source .venv/bin/activatepio コマンドがプロジェクトローカル(.venv 内)を指すようになります。
{
"terminal": {
"detect_venv": {
"on": {
"directories": [".env", "env", ".venv", "venv"],
"activate_script": "default"
}
},
}
}
最後に .gitignore に .venv/ を追加しておきます。
clangd の構成
clangd を構成するためプロジェクトのルートに .clangd ドットファイルを新規作成して次のようにします。Compiler は構成するプロジェクトに合わせてください(識別なのでここは厳密に設定しなくても大丈夫なのかもです)
CompileFlags:
Compiler: xtensa-esp32s3-elf-gcc
Add: [-DEXAMPLE_DEFINE1=1, -DEXAMPLE_DEFINE2]
Remove:
- -m*
- -fstrict-volatile-bitfields
- -fno-tree-switch-conversion
CompilationDatabase: .pio/build/esp32-s3-devkitc-1
Remove はコンパイルコマンドから clang(d) にとって不要なオプションを削除する定義です。ESP32 系は gcc でコンパイルされますので clang で使えないオプションを削除するなどしています。お好みで調整してください。
CompilationDatabase でこの後生成する compile_commands.json が配置されるディレクトリを設定しています。
compile_commands.json の生成
.clangd の CompilationDatabase で指定したディレクトリに、PlatformIO (pio) で compile_commands.json を生成させます。 compiledb というタスクが標準で定義されています。
Zed のターミナルから次のように入力します。
pio run -t compiledb
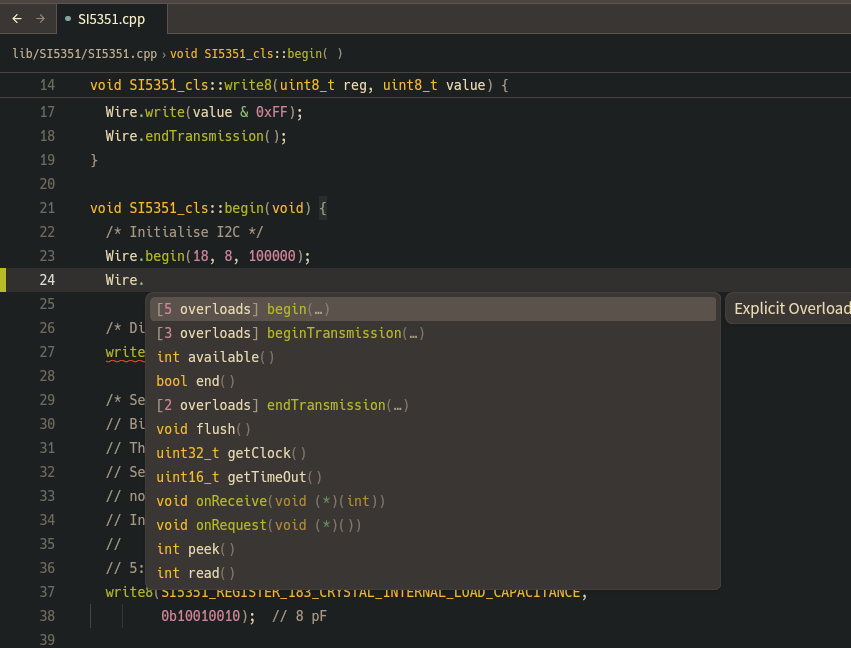
この操作で .pio/build/esp32-s3-devkitc-1/compile_commands.json が生成されたのを確認して、Zed から src/main.cpp などを開くと clangd LSP が自動起動して僅かに待つと補完が効くようになります。
以後、ライブラリやソースコードファイルの追加が合った場合は、pio run -t compiledb するイテレーションになります。
基本的にはここまでの手順となります。想定通り動作しているようであれば以下の手順は不要です。
compile_commands.json のパッチ
2025-12 現在、PlatformIO が標準で生成する compile_commands.json は次のような問題があり Zed 上のソースコードに多数のエラーや警告が出力されます。
- プロジェクトの
lib/配下のソースコードに適切な CC や include パスが設定されない。 - いくつか pio で改善する環境変数(
env.Replace(COMPILATIONDB_INCLUDE_TOOLCHAIN=True)はあるが、PlatformIO に複数のツールチェインを入れている場合、全ての include パスに入ってしまう。
$ ls -laF ~/.platformio/packages | grep toolchain
$ drwx------ 6 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 10月 13 2024 toolchain-esp32ulp/
$ drwx------ 7 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 9月 16 2024 toolchain-riscv32-esp/
$ drwx------ 7 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 9月 16 2024 toolchain-xtensa-esp32s3/
うちの環境では PlatformIO に 3 つツールチェインの登録があるため、 include パスが混乱して困ったことになっていました。 (platformio/builder/tools/piobuild.py#L131-L149)
そこでこれ以降はいささかハックではありますが、生成された compile_commands.json にパッチをあてる PlatformIO タスクを定義して解決します。(通常のビルドには影響しないようにしています)
platform.ini に次の行を追加:
[env:esp32-s3-devkitc-1]
# ..snip..
extra_scripts = pre:pio_fix_compiledb.py
プロジェクトルートに pio_fix_compiledb.py ファイルを新規作成して次のようにします。
# SPDX-License-Identifier: CC0-1.0
# pyright: reportMissingImports=false, reportUndefinedVariable=false
# flake8: noqa
"""
Utility build hook to generate and fix a compile_commands.json suitable for
clangd. Prepares the compilation database and propagates -I flags to library
entries under `lib/`.
Additionally, in environments with multiple toolchains installed, this script restricts
include paths to a single specified toolchain to ensure deterministic include
resolution.
Usage (must be run as a pair):
pio run -t compiledb && pio run -t fix_compiledb
Run `compiledb` first, then `fix_compiledb`.
Version Info (pio --version)
PlatformIO Core, version 6.1.18
"""
import glob
import json
import os
import sys
import shlex
Import("env") # type: ignore
def pre_compiledb_actions(toolchain, framework_libs=None):
"""
Prepare compile_commands.json for clangd:
- restrict CPPPATH to the specified toolchain and Arduino framework libs
- set COMPILATIONDB_PATH to the build directory
framework_libs_subdirs: optional list of sub-path patterns under PROJECT_PACKAGES_DIR
e.g. [os.path.join("arduinoespressif32", "libraries")]
"""
print("start pre_compiledb_actions")
# turn off default toolchain includes
env.Replace(COMPILATIONDB_INCLUDE_TOOLCHAIN=False)
# restrict CPPPATH to xtensa-esp32s3-elf include paths to avoid mixing toolchains.
toolchain_paths = [
p for p in env.DumpIntegrationIncludes().get("toolchain", []) if toolchain in p
]
# add path(s) to Arduino framework libraries (support multiple framework dirs)
packages_dir = env.get("PROJECT_PACKAGES_DIR")
framework_libs = framework_libs or []
framework_libs_dirs = []
for sub in framework_libs:
# join packages_dir with the provided sub-path pattern and glob
pattern = os.path.join(packages_dir, sub)
framework_libs_dirs.extend(glob.glob(pattern))
src_paths = []
for libraries_dir in framework_libs_dirs:
src_paths.extend(glob.glob(os.path.join(libraries_dir, "*", "src")))
libs_path = list(set(src_paths))
# replace CPPPATH for compiledb only
env.Replace(CPPPATH=toolchain_paths + libs_path)
# create compile_commands.json
env.Replace(COMPILATIONDB_PATH=os.path.join("$BUILD_DIR", "compile_commands.json"))
print("completed pre_compiledb_actions")
def fix_compiledb_action(*args, **kwargs):
"""
Post-process compile_commands.json:
- find the entry for the given project-relative source (args[1])
- extract its -I include flags and append missing ones to entries under 'lib/'
- write the file back only if modifications were made
"""
print("start fix_compiledb_action")
compile_commands_dir = os.path.normpath(args[0])
src_main = os.path.normpath(args[1])
compile_commands_path = os.path.join(compile_commands_dir, "compile_commands.json")
if not os.path.isfile(compile_commands_path):
print(
f"fix_compiledb_action: compile_commands.json not found at {compile_commands_path}",
file=sys.stderr,
)
return
compile_commands = []
with open(compile_commands_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
compile_commands = json.load(fp)
match = next(
(
entry
for entry in compile_commands
if os.path.normpath(entry.get("file") or "") == src_main
),
None,
)
if not match:
print(f"fix_compiledb_action: no match {src_main}", file=sys.stderr)
return
cmd = match.get("command") or " ".join(match.get("arguments", []))
tokens = shlex.split(cmd)
includes = [t for t in tokens if t.startswith("-I")]
# propagate -I flags to entries under 'lib/'
lib_count = 0
if includes:
for entry in compile_commands:
rel = os.path.normpath(entry.get("file")).replace(os.sep, "/")
if rel.startswith("lib/"):
original_cmd = entry.get("command") or ""
existing_tokens = shlex.split(original_cmd)
# only append tokens that are not already present to avoid duplication
to_append = [inc for inc in includes if inc not in existing_tokens]
if to_append:
entry["command"] = original_cmd + (" " + " ".join(to_append))
lib_count += 1
if lib_count:
with open(compile_commands_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
json.dump(compile_commands, fp, indent=2)
print(
f"Appended includes to {lib_count} lib entries in {compile_commands_path}"
)
print("completed fix_compiledb_action")
# pio run -t compiledb
if "compiledb" in COMMAND_LINE_TARGETS:
# Running `pio run -t compiledb` alone can aggregate include paths from all
# installed toolchains; to avoid that we explicitly restrict to a single
# toolchain here and collect includes only for it.
pre_compiledb_actions(
# ls -laF ~/.platformio/packages | grep toolchain
# drwx------ 6 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 10月 13 2024 toolchain-esp32ulp/
# drwx------ 7 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 9月 16 2024 toolchain-riscv32-esp/
# drwx------ 7 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 9月 16 2024 toolchain-xtensa-esp32s3/
# specify exactly one toolchain identifier, e.g. "xtensa-esp32s3-elf"
"xtensa-esp32s3-elf",
# ls -laF ~/.platformio/packages | grep frame
# drwx------ 6 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 10月 14 2023 framework-arduino-gd32v/
# drwx------ 6 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 9月 16 2024 framework-arduinoespressif32/
# drwx------ 8 hiromasa hiromasa 4096 10月 13 2024 framework-espidf/
# framework library subdirs under PROJECT_PACKAGES_DIR (joined with packages_dir inside function)
[
os.path.join("framework-arduinoespressif32", "libraries"),
],
)
# pio run -t fix_compiledb
env.AddCustomTarget(
"fix_compiledb",
None,
fix_compiledb_action(
# build directory where compile_commands.json is written (COMPILATIONDB_PATH)
# .pio/build/esp32-s3-devkitc-1
os.path.join(env.get("PROJECT_BUILD_DIR"), env.get("PIOENV")),
# source file whose compile_commands entry is used to extract -I include flags
# src/main.cpp
os.path.join("src", "main.cpp"),
),
)
Gist : https://gist.github.com/h1romas4/7399dd3985bd4dae42e8c01ee343b233
ハックなのにスクリプトが大きくて見苦しいので動作確認できたら platform.ini のパスを変更して隠してしまっていいと思います…
pio_fix_compiledb.py ファイルを追加後に次のように pio コマンドで fix_compiledb タスクを起動して、compile_commands.json にパッチをあてます。
pio run -t fix_compiledb
タスク終了後、Zed 上で開いている *.cpp や *.c を一度すべて閉じてから、main.cpp などを開き直すと、LSP が再起動 & compile_commands.json が再読込にて晴れてクリーンな補完が効くようになるはずです。
(重要)ソースコードに新規追加があった場合は次のように compile_commands.json を生成・パッチしなおして同様にソースコードを開き直せばうまくいきます。
pio -t compiledb
pio -t fix_compiledb
# 一行でかく版 (Linux)
pio -t compiledb && pio -t fix_compiledb
PlatformIO タスク dependencies を使えば fix_compiledb を自動起動できそうな気がしましたが、、うまくいかなかったので 2 コマンドにて…
パッチのスクリプトは Windows のパス区切りの違いなども気をつけてみましたが、期待通り動作しない場合は .pio/build/esp32-s3-devkitc-1/compile_commands.json を確認してスクリプトを調整してください。
また、${HOME}/.platformio 以下にある依存を変更・追加する場合はスクリプトの次の定義を修正してください。
[
os.path.join("framework-arduinoespressif32", "libraries"),
],
また、esp32-s3-devkitc-1 値が異なる場合は .clangd のパスを修正お願いします。
CompileFlags:
# ...snip...
CompilationDatabase: .pio/build/esp32-s3-devkitc-1
というわけで、pio ハックぎみですが Zed で PlatformIO プロジェクトが扱えるようになって気分が高まりました。
Zed 良い…!